ENT Health Tips for Frequent Travelers
Many travelers prepare carefully for packing and lodging but often

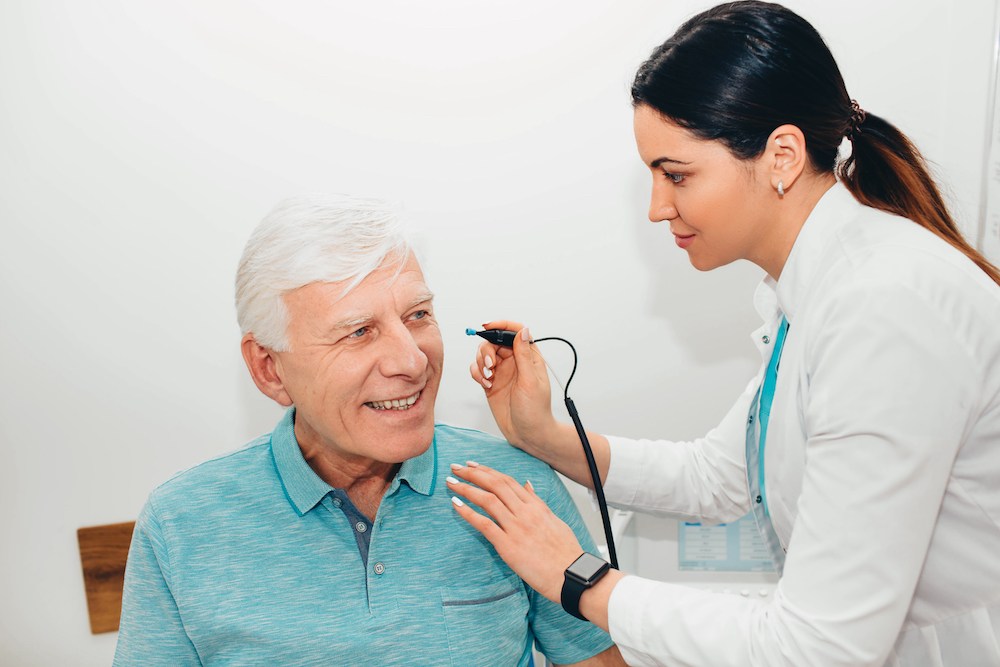
Many travelers prepare carefully for packing and lodging but often

Spring brings renewal and warmer weather, but for many of us, it also
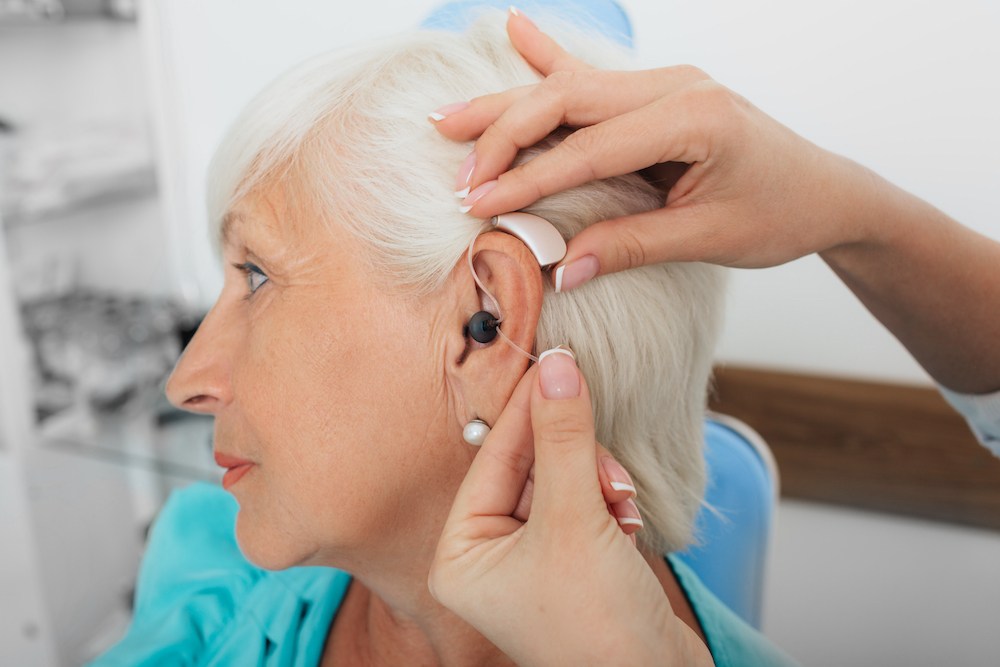
Even as winter begins to fade, unpredictable cold spells and moisture